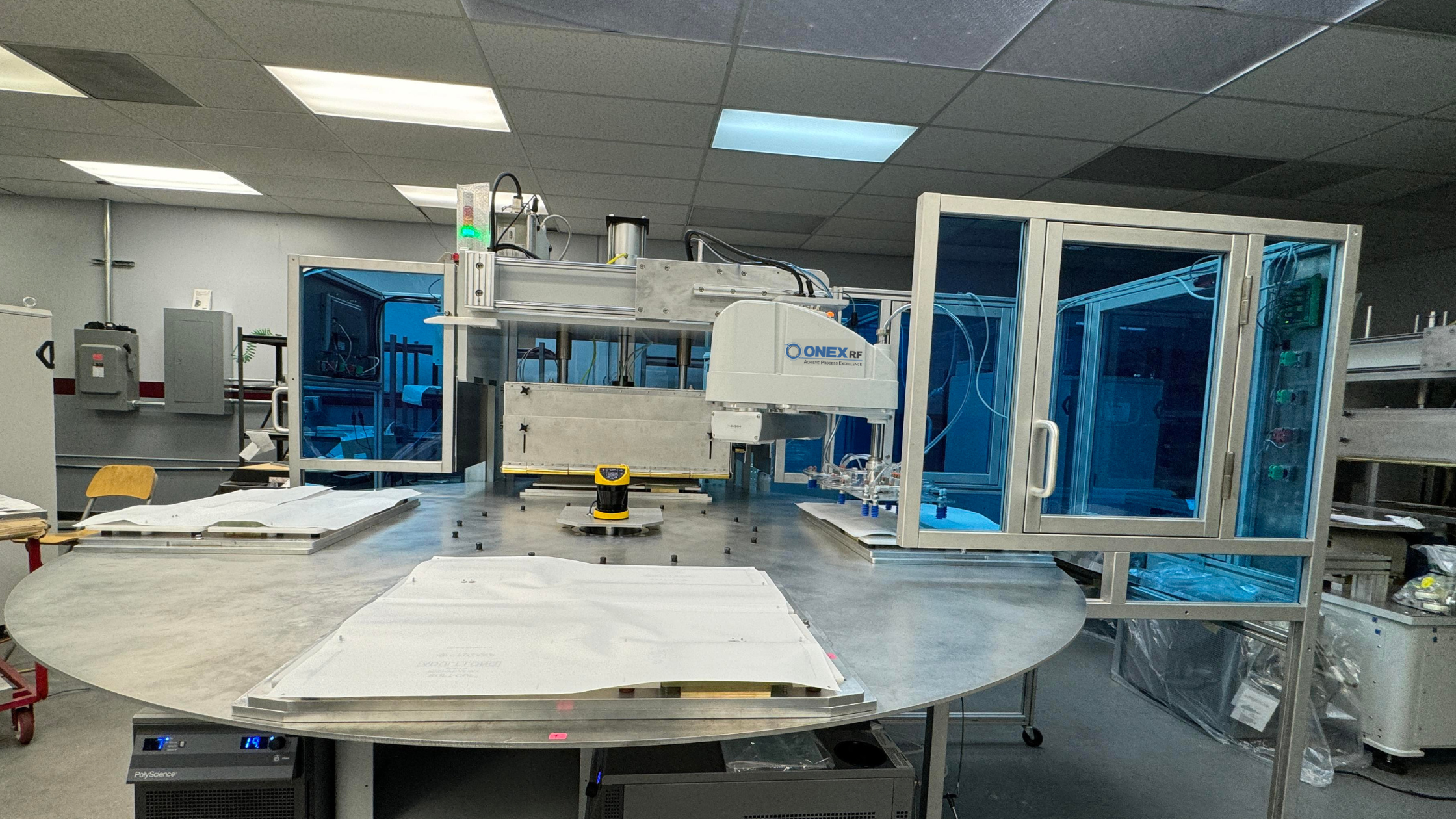
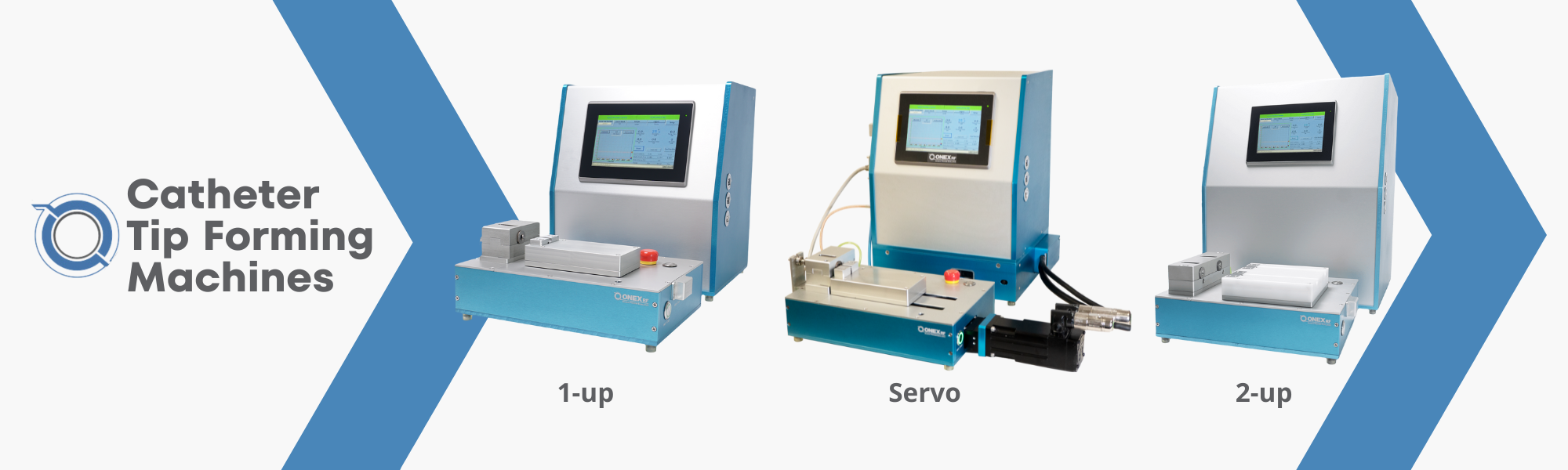
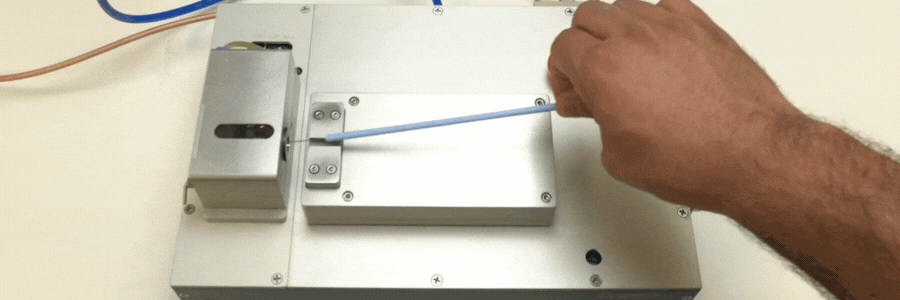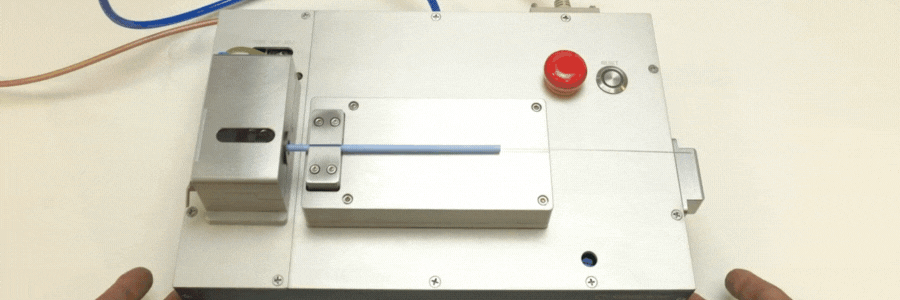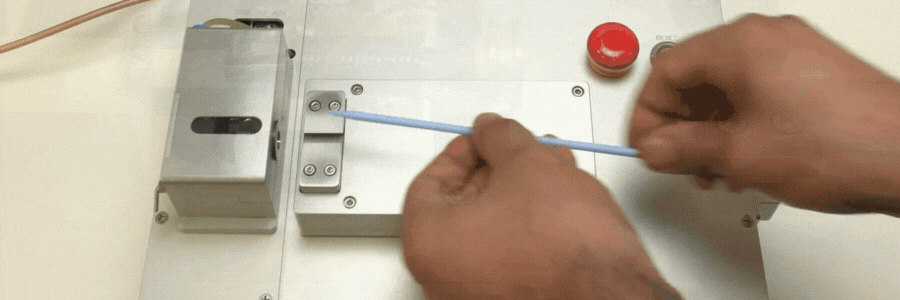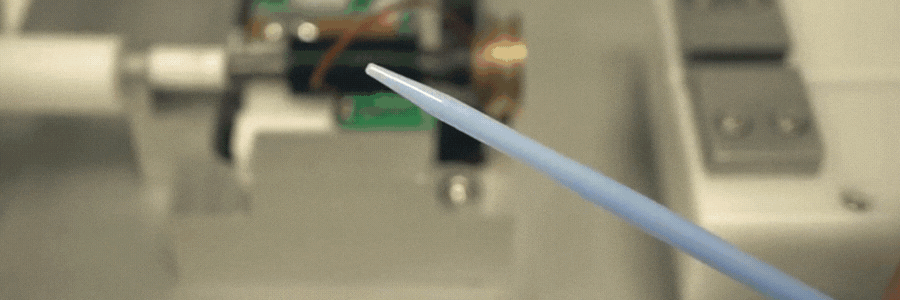
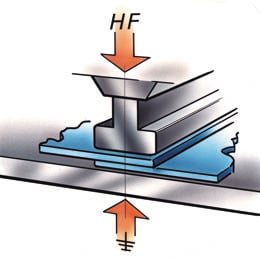
Catheters are vital components in the realm of modern medicine, facilitating a wide array of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. The intricate process of catheter manufacturing involves various stages, and one key aspect is the catheter tip forming process, where tubing is inserted into a heated mold. This article explores the RF (Radio Frequency) catheter tip forming process, shedding light on its benefits, applications, and the role it plays in ensuring precision and efficiency in medical device manufacturing.
Understanding the Catheter Forming Process
Catheter forming is a crucial step in the overall catheter manufacturing process. It involves inserting tubing into a heated mold, and after a series of melting and cooling cycles, the material is removed, leaving behind the final catheter shape. The choice of mold and heating method is pivotal in determining the efficiency and precision of this process.
RF Induction Heating in Catheter Forming
RF induction heating has emerged as a preferred method for catheter tip forming process due to its speed and control. In this process, metal molds are placed inside a coil and heated by using RF-induced current, allowing for rapid heating and precise temperature control with close-loop thermocouple feedback. Alternatively, conventional heating methods can also be employed. For certain applications, glass molds may be utilized for catheter tip forming or bonding.
The Benefits of ONEX RF Catheter Tipping
1. Fast Heating and Cooling
One of the standout advantages of RF catheter tipping is its exceptional speed in heating and cooling. This rapid temperature change capability translates to efficient production processes with shorter cycle times. The catheter material is inserted into the metal mold (tipping die) while the die is induction heated to the required temperature in a matter of seconds, providing significant process control in achieving the perfect desired shape.
2. Consistent Repeatable Process
Beyond its speed, the RF induction coil, designed and perfectly positioned over the die, ensures a consistent and repeatable process. Whether using RF induction vs. conventional heating methods, the RF induction method offers faster heating and cooling and better process control. This results in uniform and reliable products, a critical factor in medical applications where the catheter's performance and reliability are paramount.
3. Closed-Loop Process Control
The key factors in RF catheter tipping process require closed-loop process control, such as die temperature, coil position over the die, and forming stroke. ONEX RF tipping systems are known for the use of precise die temperature feedback and sensors for mechanical position feedback of coil and forming stroke. This meticulous control ensures optimal results, enhances the quality of the final product, and minimizes the risk of defects or inconsistencies.
Applications of RF Catheter Forming
The RF catheter forming process finds applications across various types of catheters, each designed for specific medical purposes. Some notable applications include:
1. Cardiac Catheters
RF catheter forming is widely employed in the manufacturing of cardiac catheters. These catheters are utilized in diagnostic and therapeutic procedures related to the heart, and the precision offered by RF tip-forming of the distal and proximal ends of catheters is particularly beneficial in ensuring the accuracy of these delicate procedures.
2. Vascular Catheters
Vascular catheters, designed for procedures involving blood vessels, benefit from the efficiency of RF catheter forming and bonding the soft tips in a single cycle. The fast heating and cooling capabilities contribute to quicker production cycles, meeting the demands of high-volume manufacturing without compromising precision.
3. Urinary Catheters
Catheters used in urinary procedures require a high level of precision and smoothness. RF catheter forming provides the consistency needed to meet the patient's comfort and medical standards in the production of urinary catheters.
4. Neurological Catheters
In the realm of neurological procedures, where precision is paramount, RF catheter forming of microcatheters ensures that catheters used in these applications are manufactured with the utmost accuracy. This is critical for procedures involving the delicate structures of the nervous system.
5. Dilator and Sheaths
The dilators play a crucial role in stretching the opening in the sensitive skin and blood vessels allowing for the seamless introduction of the sheath. After removing the dilator, the sheath acts as a secure tunnel for of various catheter introductions. The dilators with long-tapered tips are produced using long RF induction coils in combination with custom up to 4" long tipping dies, and servo-controlled long-stroke slides, which offer excellent forming speed control.
Advancements in RF Catheter Forming Technology
As technology continues to advance, so does the field of RF catheter tip forming machines. Innovations in catheter materials, mold manufacturing techniques, and process monitoring with data collection methods contribute to further enhancing the efficiency and precision of the catheter manufacturing process. Some notable advancements include:
1. Material Innovations
The development of new high-temp, flexible materials that meet the requirements of medical procedures introduces new challenges and possibilities for molding catheter tips using RF induction heating technology. These materials require a higher temperature for melting and forming the catheter tips and have a very narrow band of process control. This requires collaboration between the R&D teams and tipping machine producers to achieve a good quality product.
2. Mold Designs for Specialized Applications
Customized mold designs for specific catheter applications have become more prevalent. These designs require consideration of material shrinkage and tight tolerances to cater to the unique requirements of different customer requirements, ensuring that the formed catheters meet the highest standards of precision and functionality.
3. Integration of Smart Technologies
The integration of smart technologies, such as vision sensors and automation, into RF catheter-forming equipment enhances the overall control and monitoring of the process. This results in improved quality control, reduced variability, and increased efficiency in manufacturing.
Quality Control Measures in RF Catheter Forming
Ensuring the quality and reliability of catheters produced through RF catheter tip forming involves implementing robust quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process. These measures include:
1. Regular Inspections
Routine inspection and cleaning of the molds and formed catheters help identify any issues or abnormalities that could affect the quality of the final product. This proactive approach ensures that the manufacturing process remains in compliance with medical standards.
2. Testing Protocols
Rigorous testing protocols are implemented to assess the physical and functional characteristics of the formed catheters. This includes testing for flexibility, tip shape, shaft strength, and other factors relevant to the specific application of the catheter.
3. Process Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of the RF energy used for heating the mold and the temperature feedback in the RF tipping process is essential for maintaining consistency. By closely monitoring key variables, manufacturers can identify trends or deviations and make real-time adjustments to ensure optimal results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ONEX RF catheter tipping machines play a vital role in elevating the standards of catheter manufacturing. Its benefits in terms of speed, precision, and consistency contribute to the production of reliable medical devices crucial for patient care. As the healthcare industry evolves, the role of RF catheter forming is likely to expand, further cementing its status as a cornerstone in modern medical device manufacturing. Whether in cardiac, vascular, urinary, or neurological applications, the RF catheter tipping process continues to shape the landscape of medical innovation, ensuring that catheters meet the highest standards of safety and performance.